Unit 4: Cultural Patterns and Processes
Types of Diffusion
- Relocation and expansion—including contagious, hierarchical, and stimulus expansion—are types of diffusion.
Part 1 – Language
1.1 What is language?
Language is the principal method of human communication, consisting of words used in a structured and conventional way and conveyed by speech, writing, or gesture. It is a system of communication used by a particular country or community.
Language in Numbers (click to reveal)
- Countries in the world: 195
- Number of official languages in the world: 7,117
- Percentage of languages spoken by less that 1000 people: 40%
- Number of people who can speak English: 1.34 billion
- Number of people who can speak English as a ‘mother tongue’: 369.9 million
- Number of people who can speak English as a secondary language: 978.2 million
- Number of people who can speak Mandarin Chinese: 1.12 billion
- Number of people who can speak Mandarin Chinese as their native language: 921.2 million
- Number of people who can speak Mandarin Chinese as a secondary language: 198.7 million
- Third most spoken language in the world: Hindi (600 million)
- Fourth most spoken language in the world: Spanish (543 million)
- Fifth most spoken language in the world: Arabic (274 million)
- More here.
1.2 Types and Families
To be able to discuss certain linguistic types, we must list the largest language groups in the shortest terms. They are specified according to three criteria:
- Genealogical familiarity
- Structural familiarity
- Geographic distribution
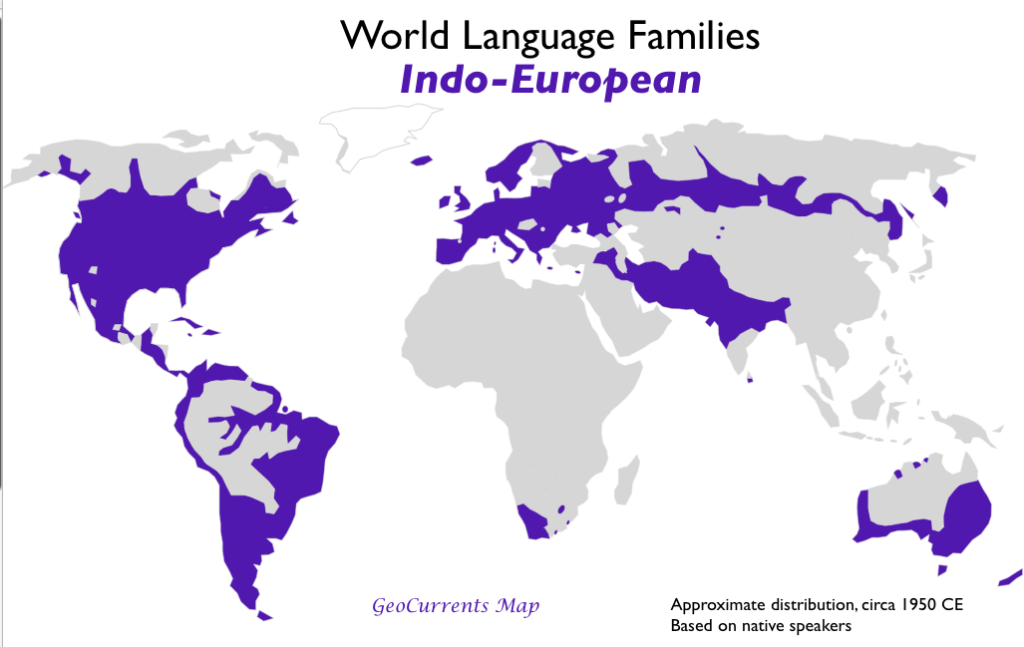
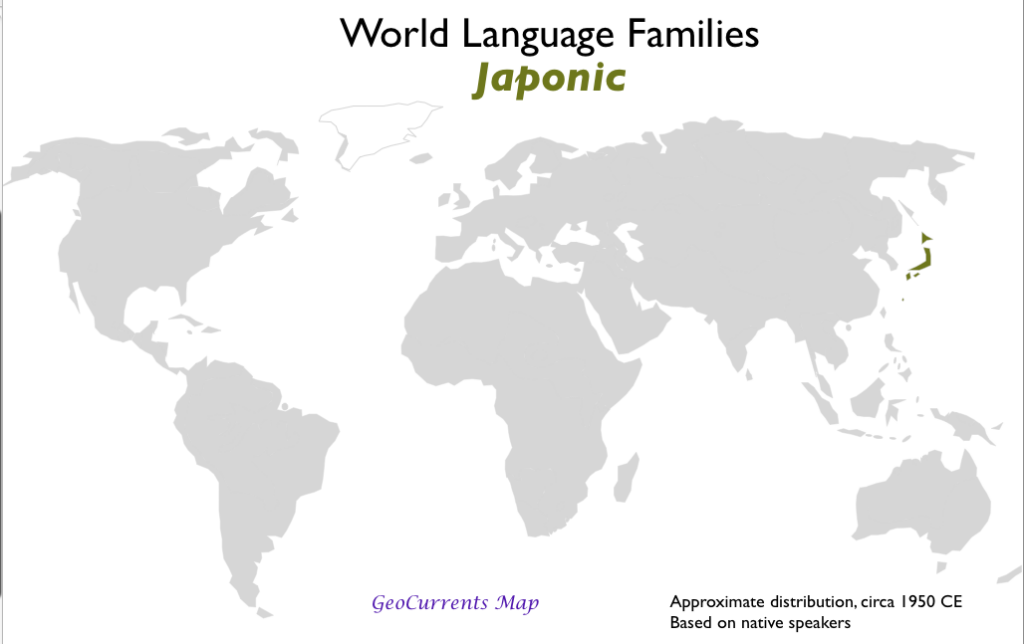
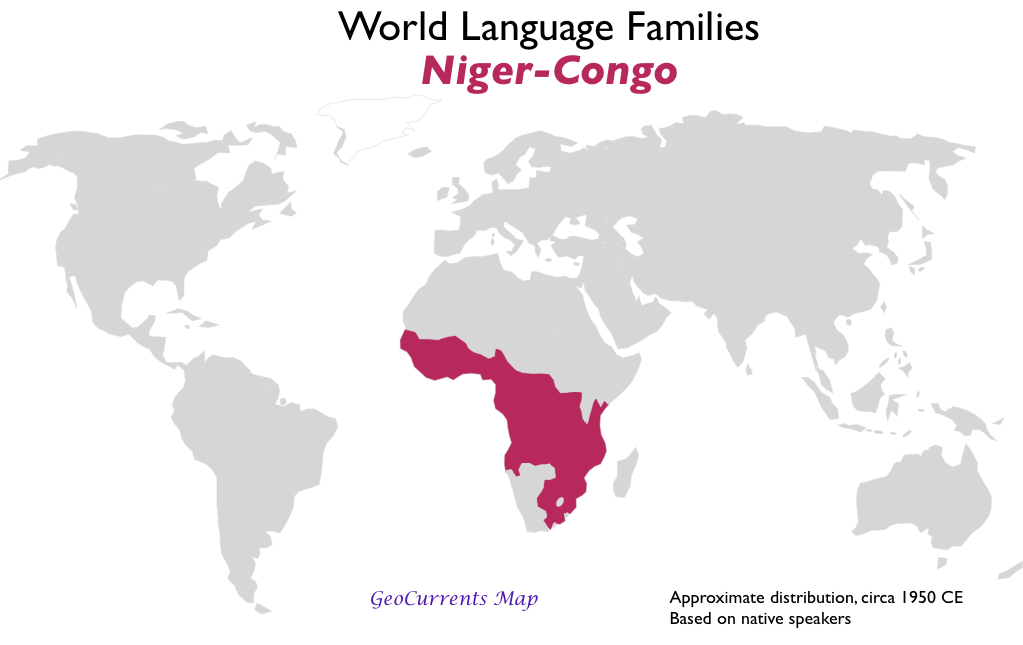
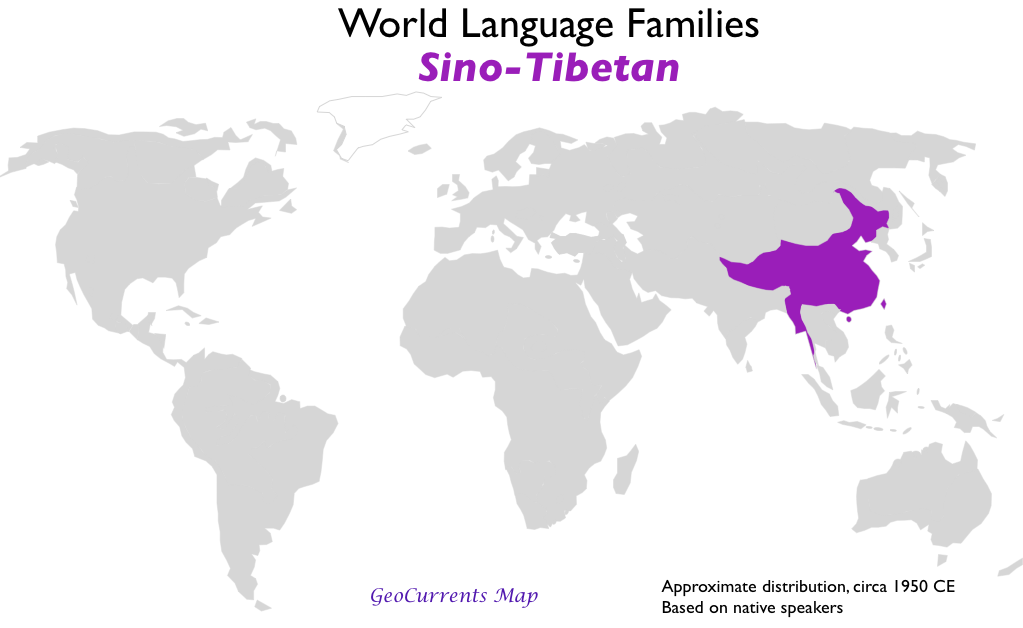
According to these criteria, the below are the important language family groups:
- Indo-European
- Sino-Tibetan
- Niger-Congo
- Afroasiatic
- Austronesian
- Altaic
- Japonic
- Austroasiatic
- Tai-Kadai
- Here is a full list.
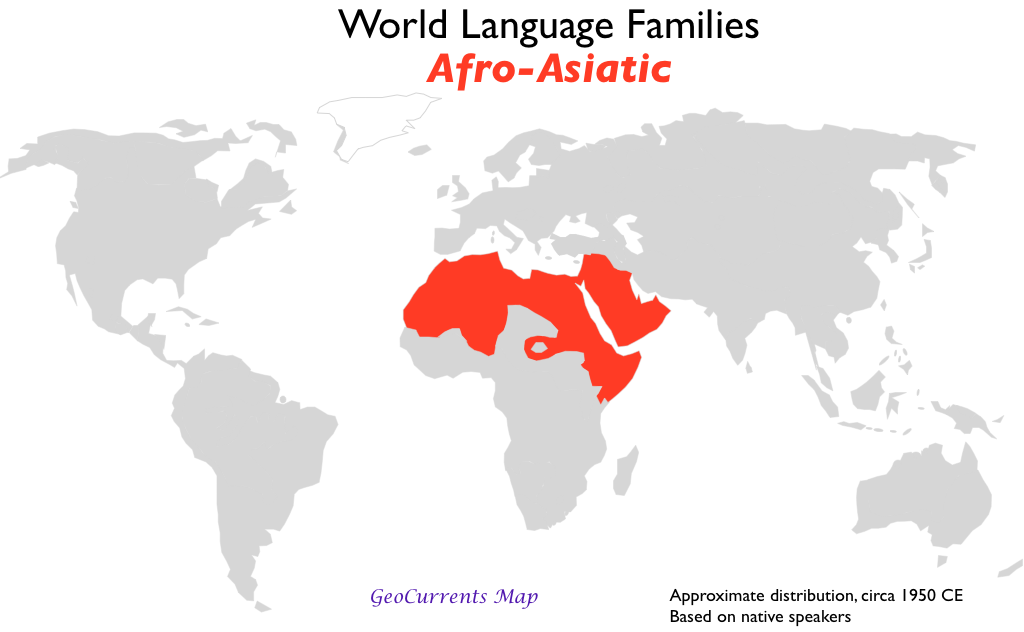
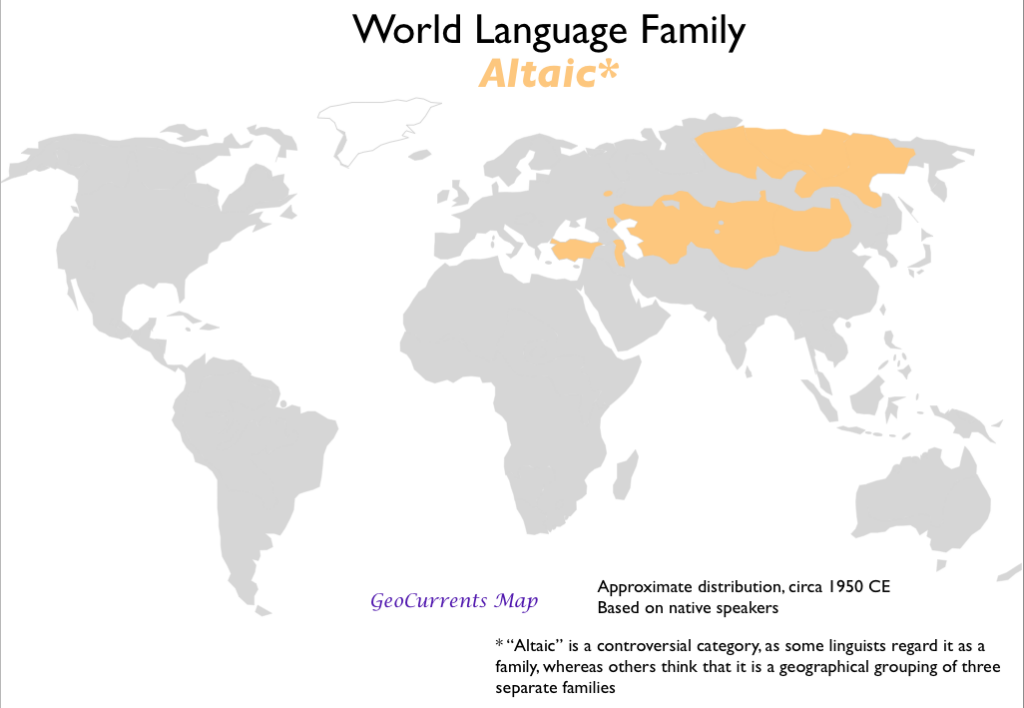
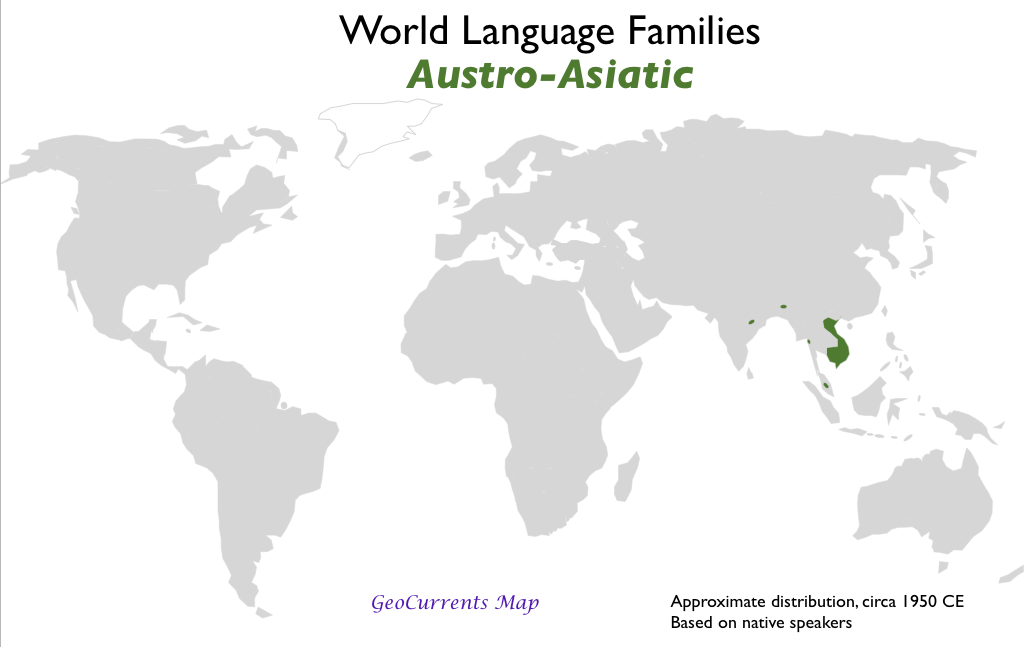
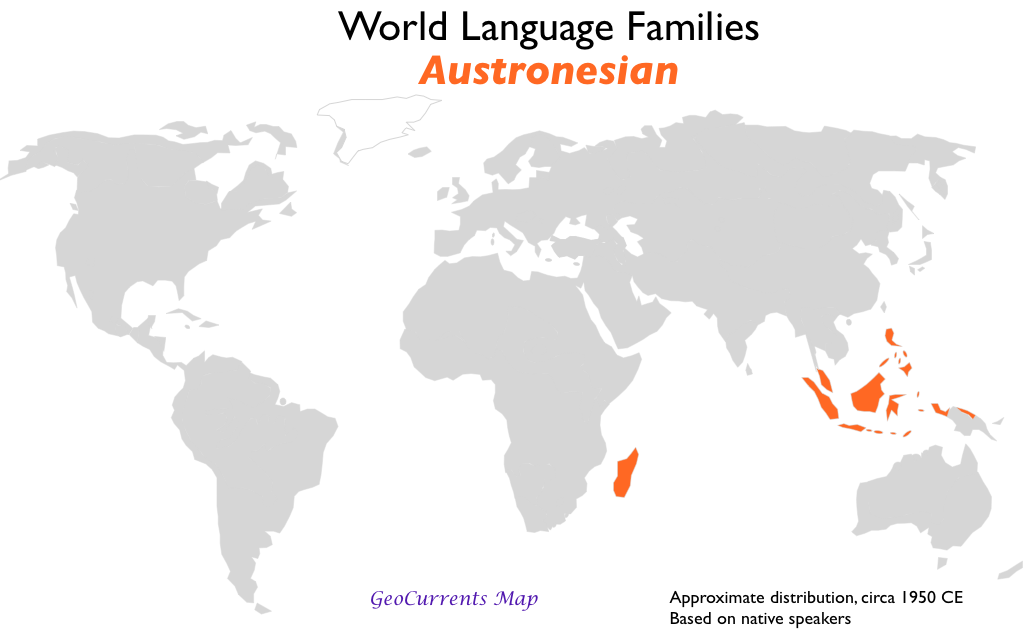
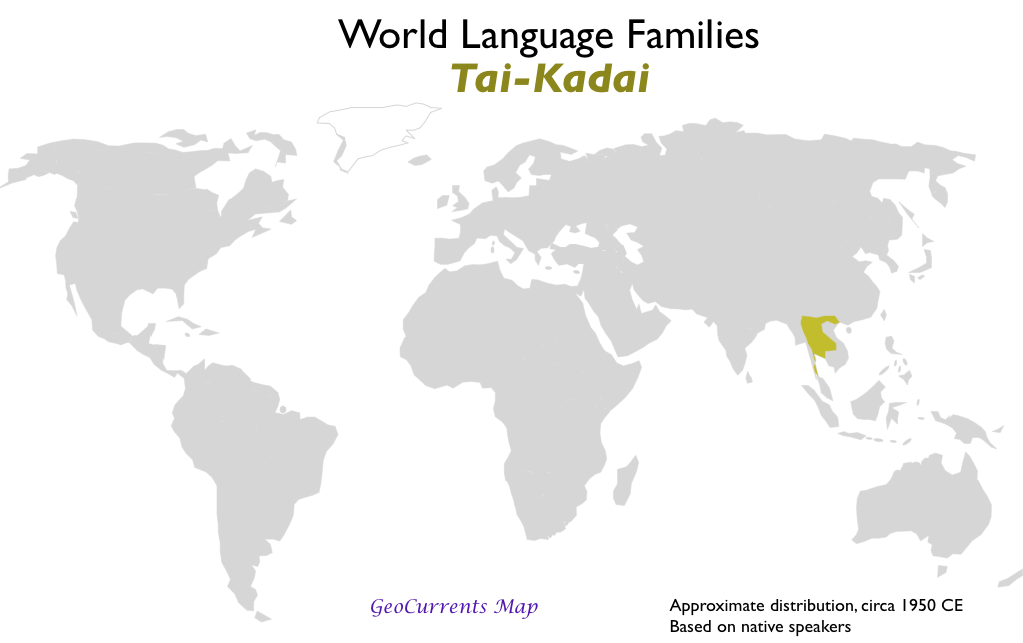
1.3 Diffusion of Language
Language diffusion is the process by which a language or its features spread from one area to another where it was not previously spoken. This process can lead to languages borrowing elements from each other and developing new ways of speaking.
Some factors that can influence language diffusion include:
- Migration: When groups of people move away from each other, their languages can branch into dialects and become isolated.
- Conquests and colonization: These can lead to the spread of a dominant language and the retreat of a minority language.
- Technological advancements: These can also lead to the spread of language features.
- Interaction with other speakers: This can influence language dynamics.
- Hierarchical diffusion: When new slang or expressions are invented in major cities and then adopted in smaller towns.
- Contagious diffusion: When new slang spreads within a group, such as a school, as friends mimic each other’s speech.
The spread of English is an example of language diffusion, as the British Empire spread the language through its colonies and geopolitical dominance.
Activity
Explore Ethnologue.com
Part 2 – Religion
2.1 What is Religion?
Religion can be defined as a personal set or institutionalized system of religious attitudes, beliefs, and practices, including the service and worship of God or the supernatural and commitment or devotion to religious faith or observance. As definitions should not be circular, it can also be described as a cause, principle, or system of beliefs held to with ardor and faith.
2.2 Types of and Major Religions
Religions can be broadly classified as follows, but please not that not religions are necessarily deemed as equal. For an example read the following:
In monotheistic belief systems, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. In polytheistic belief systems, a god is “a spirit or being believed to have created, or for controlling some part of the universe or life, for which such a deity is often worshipped”. Belief in the existence of at least one god is called theism.
| Religious Classification | What/Who Is Divine | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Polytheism | Multiple gods | Belief systems of the ancient Greeks and Romans |
| Monotheism | Single god | Judaism, Islam, Christianity |
| Atheism | No deities | Atheism |
| Animism | Nonhuman beings (animals, plants, natural world) | Indigenous nature worship (Shinto) |
| Totemism | Human-natural being connection | Ojibwa (Native American) beliefs |
To remind yourself about the major religions of the world you can look here. The largest religous groups are as follows:
| Religion | Followers (billions) | Cultural tradition | Founded |
| Christianity | 2.4 | Abrahamic religions | Judaea (Middle East) |
| Islam | 1.9 | Abrahamic religions | Arabia (Middle East) |
| Hinduism | 1.2 | Indian religions | Indian subcontinent |
| Buddhism | 0.5 | Indian religions | Indian subcontinent |
| Shinto | 0.1 | Japanese religions | Japan |
This map (click launch) allows you to explore the prevailing beliefs across the globe and also the other beliefs within the prevailing beliefs.
2.3 Diffusion
Hinduism
Hinduism is the oldest major religion originating around the Indus Valley (within modern day Pakistan) around 4,000 years ago. Hinduism diffused into Southeast Asia (mostly India) and into the island of Bali in Indonesia. There are more than 750 million followers today. Buddhism appeared in eastern India around the sixth century B.C., as a reaction to certain aspects of Hinduism (such as the caste system). It began diffusing around the third century B.C. into Nepal, and South and East Asia. There are around 350 million followers today.
Christianity
Christianity originated with the birth of Jesus near Jerusalem. It diffused rapidly (hierarchically) throughout Europe when the Roman Emperor Constantine was converted to Christianity in A.D. 312. It was diffused worldwide (relocation) through the European Age of colonialism beginning around the late 15th century. There are more than 1.5 billion followers today, more than any other religion.
Islam
Islam, the youngest of the major world religions, arose out of the teachings of Muhammad, who was born in A.D. 571 around eastern Arabia. It spread from modern day Saudi Arabia mostly by hierarchical diffusion through Arab traders into Southwest Asia and North Africa. It has also spread eastward and dominates Indonesia (the largest Muslim nation today). There are more than 1.2 billion followers today, and is the fastest growing religion (in part due to the high growth rates of the regions in which it dominates).
Activity
Show the Cradle land of the major religions on a map of the world. For example you could use a different colour for each religion. Clearly identify the cradle place or region, and the modern spread. Try to indicate how they have diffused across the globe since that point, maybe with arrows or simply a description.
You COULD add any important dates and people/events that you come accross later (this is how you access the highest levels of learning and grades.
You can use the provided map, your own, or Google MyMaps
The map below is mine but I have only completed it for one religion as an example.
Part 3 – Culture
3.1 What is culture?
Culture comprises the shared practices, technologies, attitudes, and behaviors transmitted by a society.
3.2 Cultural landscape
- Cultural landscapes are combinations of physical features, agricultural and industrial practices, religious and linguistic characteristics, evidence of sequent occupancy, and other expressions of culture including traditional and postmodern architecture and land-use patterns.
3.3 What is a cultural trait?
- Cultural traits include such things as food preferences, architecture, and land use.
3.4 Cultural practices
Cultural practices are the behaviors, customs, and activities that are passed down through generations within a specific culture or society. They can include a wide range of activities, such as:
- Consumption
- Parenting
- Interpersonal tasks
- Artistic expressions
- Practices related to religion, holidays, food, dance, clothing, language, music, crafts, and pastimes
3.5 What is a cultural pattern?
- Regional patterns of language, religion, and ethnicity contribute to a sense of place, enhance placemaking, and shape the global cultural landscape.
3.6 Diffusion of Culture
Cultural diffusion, also known as cultural blending or transcultural diffusion, is the spread of cultural practices, beliefs, or items from one culture to another. This can happen when cultures interact with each other through trade, migration, or geographical proximity.
Some examples of cultural diffusion include:
- The spread of the war chariot and iron smelting: A cultural diffusion that occurred in ancient times
- The use of automobiles and Western business suits: A cultural diffusion that occurred in the 20th century
- The Silk Road: A network of trade routes that connected China, Europe, and the Middle East, allowing cultural ideas to spread from one region to another
Some types of cultural diffusion include:
- Relocation diffusion: When people migrate and take their culture with them to a new place
- Expansion diffusion: When an idea rapidly grows in popularity and spreads across different cultures
- Forced cultural diffusion: When a conquering group forces their culture on the people they conquer
Activity
Cultural Diffusion Quiz Presentation Note Sheet.
Cultural Diffusion Quiz Presentation Note Sheet.
End of Project Quizzes.
Language, Religion, and Cultural Practices.
This is a definition based quiz.

Language, Religion, and Cultural Practices Quiz for 10th Grade