Unit 4: Cultural Patterns and Processes
Core Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
1. Define and explain cross-cultural interactions and their effects 2. Identify and describe different ways that cultural practices spread 3. Analyze historical forces that have affected cultural patterns 4. Evaluate modern forces influencing cultural exchange 5. Reflect on your own experiences with cross-cultural interactions
Introduction
Welcome to our exploration of cross-cultural interactions and cultural spread! Over the next 2 to 3 days, we’ll dive deep into how different cultures influence each other and how cultural practices move around the world. Whenever you are asked to consider something you must find someone to discuss your thoughts with at this point.
BEFORE YOU START: Buzz to the extension activity at the end and look at the recipes. Choose at least one and make a list of the ingredients you will need.
To start, let’s watch a short video to get us thinking about culture:
After watching, consider:
- What stood out to you in the video?
- Have you ever seen or heard of this kind of cultural conflict or misunderstanding?
Vocabulary List
Throughout this unit, we’ll be using these key terms:
| Cross-cultural interaction | Cultural fusion | Migration |
| Globalization | K-Pop | Cultural diversity |
| Cultural exchange | Cultural bias | Ethnocentrism |
| Cultural appropriation | Intercultural communication | Cultural diffusion |
| Silk Road | Tolerance | Multiculturalism |
Part 1: Understanding Cross-Cultural Interactions
Language diffusion is the process by which a language or its features spread from one area to another
What are cross-cultural interactions?
Cross-cultural interactions occur when people from different cultural backgrounds come into contact and exchange ideas, practices, or goods. In our globalized world, these interactions happen more frequently than ever before.
| Positive effects of cross-cultural interactions: | Negative effects of cross-cultural interactions: |
| Cultural exchange and learning | Cultural misunderstandings and conflicts |
| Technological and scientific advancements | Loss of traditional practices and languages |
| Diverse perspectives in problem-solving | Cultural appropriation |
| Economic growth through international trade | Spread of diseases |
Activity
Short note making. Share a personal experience with cross-cultural interaction. Note: – What was the context of the interaction? – What did you learn from the experience? – Were there any challenges or misunderstandings?
Part 2: How Cultural Practices Spread
Cultural practices can spread through various means:
- Migration: People moving from one place to another, bringing their customs with them.
- Trade: Exchange of goods often leads to exchange of ideas and practices.
- Conquest: Throughout history, conquering nations have imposed their culture on others.
- Media and Technology: In the modern world, ideas spread rapidly through the internet, TV, and social media.
- Education: Learning about other cultures in school or through travel.
Historical Example: The Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of trade routes connecting East and West, primarily between China and the Mediterranean region. It was active from around 200 BCE to the 15th century CE.
Effects of the Silk Road:
- Spread of technologies (e.g., papermaking from China to the West)
- Exchange of religions (e.g., Buddhism spreading from India to China)
- Culinary exchanges (e.g., noodles traveling from China to Italy)
Activity
The Silk Road Adventure Game – OPTION ONE
https://player.stornaway.io/watch/6b2527ec
| The Silk Road Adventure Game – OPTION TWO Introduction Welcome, young explorers! Today we’re going to embark on an exciting journey along the ancient Silk Road. This game will test your knowledge about this important trade route and help you learn more about the cultural exchanges that happened along the way. Game Setup This is a text-based adventure game. You’ll be presented with scenarios and choices. Your decisions will affect your journey along the Silk Road. Your goal is to successfully travel from Chang’an (modern-day Xi’an) in China to Rome, trading goods and experiencing cultural exchanges along the way. For each choice you make you must have a valid reason. Starting the Journey You are a merchant in ancient China, about to embark on a journey along the Silk Road. You start in Chang’an with 100 gold coins and must choose what goods to take with you. Choice 1: Select your primary trade good 1. Silk 2. Tea 3. Porcelain > Silk was the most famous trade good on the Silk Road, but tea and porcelain were also important exports from China. The Journey Begins As you leave Chang’an, you encounter other merchants. They tell you about the dangers and opportunities ahead. Choice 2: How do you prepare for the journey? 1. Hire extra guards for protection 2. Buy a camel for desert travel 3. Learn some foreign languages > Each choice has its benefits. Guards offer protection, camels are crucial for desert travel, and knowing languages can help in negotiations and cultural exchanges. Desert Crossing You’ve reached the treacherous Taklamakan Desert. This part of the journey is known for its harsh conditions. Choice 3: How do you cross the desert? 1. Take the northern route around the desert 2. Take the southern route around the desert 3. Attempt to cross directly through the desert > The northern and southern routes were safer but longer. Crossing directly was dangerous but could be faster if successful. Cultural Exchange You’ve reached the city of Samarkand, a major hub on the Silk Road. Here, you encounter merchants from Persia. Choice 4: How do you interact with the Persian merchants? 1. Trade goods with them 2. Learn about their culture and religion 3. Ignore them and continue your journey > Cultural exchange was a crucial aspect of the Silk Road. Trading, learning about other cultures, and religious exchanges were common. Final Stretch You’ve made it to the Mediterranean Sea. You’re almost at Rome, but you need to decide how to complete your journey. Choice 5: How do you reach Rome? 1. Take a ship across the Mediterranean 2. Continue by land through Constantinople 3. Hire a guide to take you through unfamiliar territory > Sea routes became increasingly important in later years of the Silk Road. Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) was a crucial link between East and West. Conclusion Congratulations! You’ve completed your journey along the Silk Road. Based on your choices, you’ve not only traded goods but also experienced the rich cultural exchanges that made the Silk Road so important in history. Remember, the real Silk Road wasn’t just about silk or trade – it was a complex network that facilitated the exchange of ideas, technologies, religions, and cultures between East and West over many centuries. Explain your choices and reasons. |
Part 3 – Historical Forces Affecting Cultural Patterns: The Impact of Colonialism
Introduction
Colonialism, the practice of one country taking control of another, has had profound and lasting effects on cultural patterns around the world. We will explore how colonialism impacted different regions and provide examples of colonial influences that can still be seen today.
How Colonialism Affected Cultural Patterns
1. Language
One of the most significant impacts of colonialism was on language:
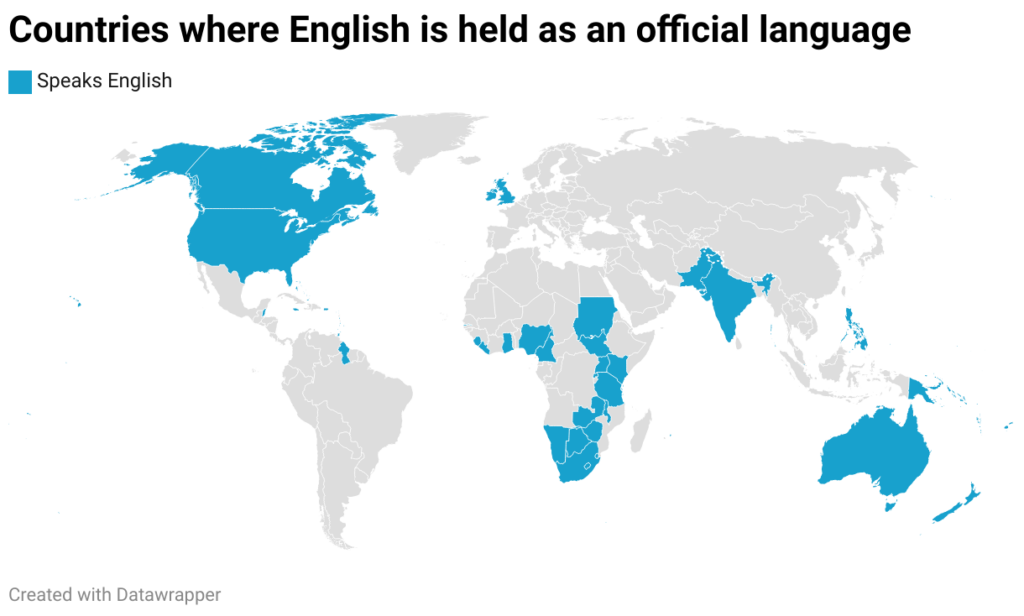
- Many former colonies still use the language of their colonizers as an official language.
- Examples: English in India and Nigeria, French in Senegal and Vietnam, Spanish in Latin America.
2. Religion
Colonialism often led to the spread of the colonizer’s religion:
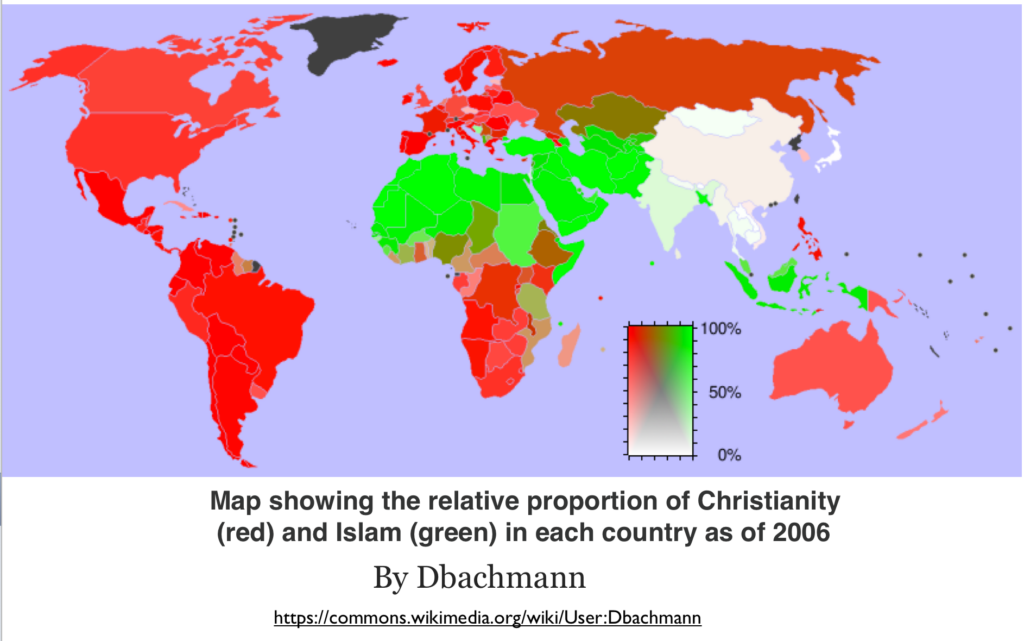
- Christianity spread to many parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- Islam expanded in some regions due to Arab colonization.
3. Education Systems
Colonial powers often imposed their educational models:
- British-style education systems in former British colonies.
- French-style lycées in former French colonies.
4. Governance and Legal Systems
Many former colonies retained aspects of their colonizers’ systems:
- Common law systems in former British colonies.
- Civil law systems in former French and Spanish colonies.
5. Cultural Fusion
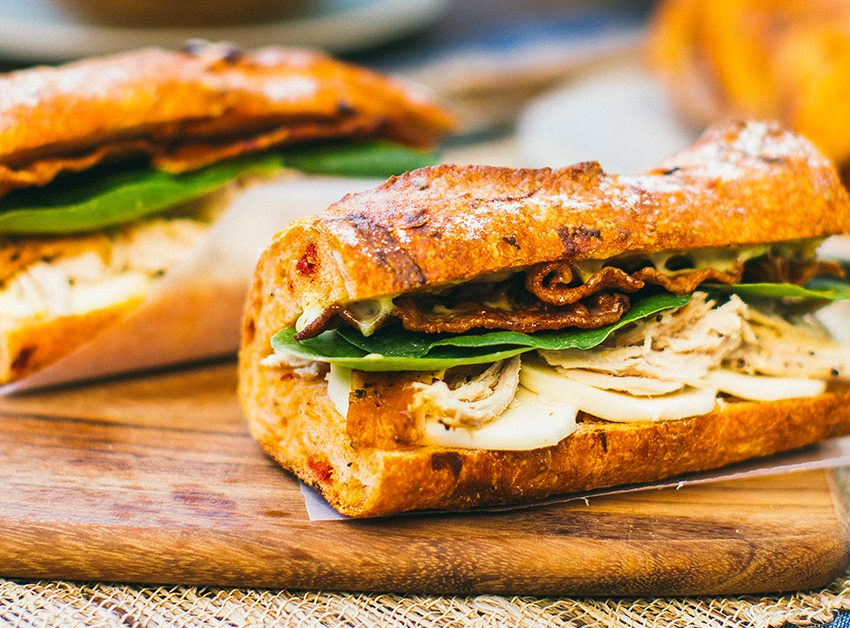
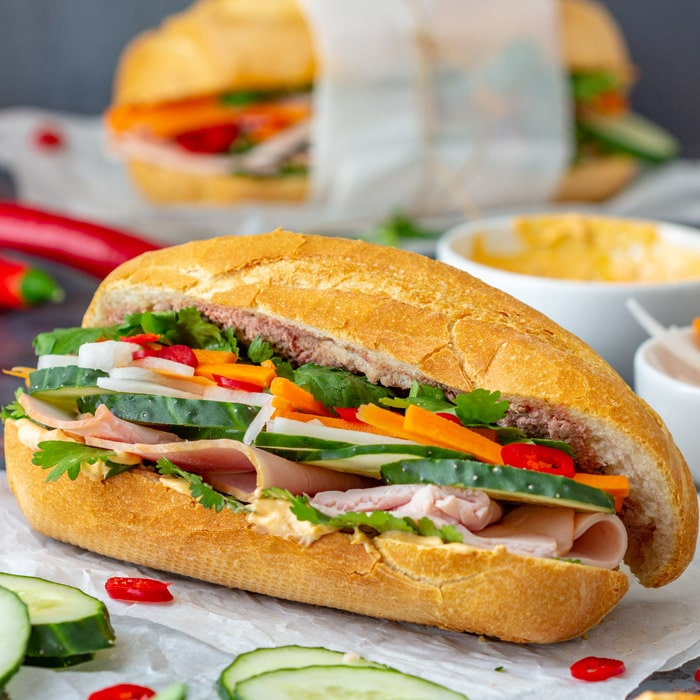


Colonialism led to the blending of local and colonial cultures:
- Cuisine: Indian curry in Britain, Vietnamese banh mi (influenced by French baguettes).
- Music: Development of genres like reggae (Jamaica) and samba (Brazil).
6. Economic Systems
Colonial economic patterns often persisted after independence:
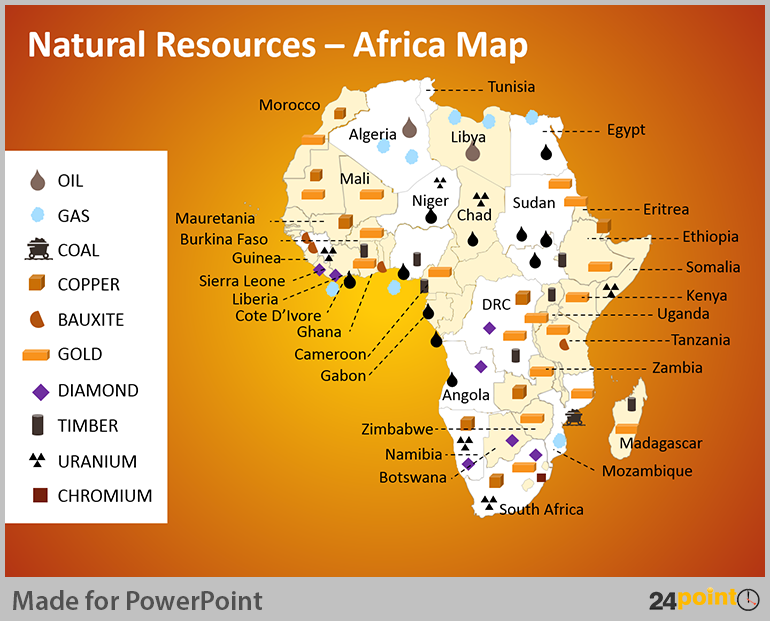
- Cash crop economies in many African and Caribbean nations.
- Resource extraction economies in various former colonies.
Examples of Colonial Influence in Different Cultures
United States
- English as the primary language
- Common law legal system
- Christmas as a major holiday (Christian influence)
- Sports like baseball and American football (derived from British games)
India
- English as an official language and lingua franca
- Cricket as a popular sport
- Railway system developed during British rule
- Tea culture influenced by British tastes
Video: “The Unmaking of India: How the British Impoverished the World’s Richest Country” (16 minutes)
Mexico
- Spanish as the official language
- Catholicism as the predominant religion
- Mestizo culture (mix of indigenous and Spanish influences)
- Many city names with Spanish origins (e.g., San Diego, Los Angeles)
– Video: “What was life like in colonial Mexico?” (2 minutes)
Nigeria
- English as the official language
- Football (soccer) as a popular sport
- Educational system based on the British model
- Christian and Muslim influences alongside traditional beliefs
Video: “Has colonisation continued to shape Nigeria’s politics?” (5 minutes)
Trade and Cultural Exchange
Trade has been a major driver of cultural exchange throughout history. Let’s look at some examples:
- The spice trade: Introduced new flavors and cooking techniques to different parts of the world.
- The tea trade: Spread tea culture from China to Europe and beyond.
- The coffee trade: Brought coffee from Ethiopia to the Middle East, then to Europe and the Americas.
Conclusion
Colonialism has left an indelible mark on cultural patterns worldwide. Its effects can be seen in language, religion, education, governance, and many other aspects of daily life. Understanding these influences helps us appreciate the complex tapestry of global cultures and the historical forces that shaped them.
Video: “The Effects of Colonialism” by Crash Course (13 minutes)
Activity
Map Colonial Territories: Create a world map showing the extent of European colonialism at its peak (around 1914). Color-code the map to show which European countries controlled which territories.
Examples to include:
British Empire in India, parts of Africa, and the Caribbean, French colonies in North Africa and Indochina, Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia), Portuguese colonies in Africa and South America.
Questions – Global Cultural Exchange: Ancient to Modern
https://forms.gle/emGjK6GTXhzEXh387
Part 4 – Modern Forces Affecting Cultural Patterns
Globalization and Its Effects
Globalization has dramatically accelerated cross-cultural interactions in recent decades.
After watching, consider:
- How has globalization affected cross-cultural interactions in the modern world?
- Can you think of examples of globalization in your daily life?
Case Study: K-Pop Global Phenomenon
K-Pop (Korean Popular Music) has become a global cultural force. Let’s explore its spread and impact:
- Origins in South Korea
- Spread through social media and online platforms
- Influence on fashion, language learning, and tourism
- Cultural appropriation concerns
Activity
Cultural Fusion
Create a fictional “fusion” product that combines elements from two different cultures. This could be a food item, a style of music, or a fashion trend. Discuss the potential positive and negative impacts of this fusion. Draw it or create a short ad campaign (phone video?), or make a package design.
Technology and Cultural Spread
The internet and social media have revolutionized how cultural practices spread:
- Viral trends and challenges
- Online language learning platforms
- Virtual cultural experiences (e.g., virtual museum tours)
- Global online communities
Activity
Digital Cultural Exchange
Explore a cultural practice from another country using online resources, then teach this practice to someone else.
Questions – Modern Forces Affecting Cultural Patterns
https://forms.gle/9Q39xLyyyScdfnfW6
Part 5 – Navigating Cross-Cultural Interactions
Tips for Effective Cross-Cultural Communication:
- Be open-minded and respectful
- Learn about other cultures
- Be aware of your own cultural biases
- Practice active listening
- Be patient and ask questions when unsure
Activities
Effective Cross-Cultural Communication: In our increasingly globalized world, the ability to communicate effectively across cultures is a vital skill. This activity will help you understand and practice key aspects of cross-cultural communication.
Activity Overview:
This activity consists of three parts: A. Cultural awareness self-assessment B. Case study analysis C. Role-playing exercise
Quiz: How Culturally Savvy Are You?
How Culturally Savvy Are You?
Cultural awareness self-assessment:
Welcome to this personality quiz that will help you understand how well you navigate cross-cultural interactions! This quiz will assess your knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors in various cultural scenarios. Remember, there are no right or wrong answers – just be honest about your experiences and thoughts.

Part B: Case Study Analysis
Scenario
A U.S. company is expanding its operations to Japan. During a video conference, the American team proposes a new marketing strategy. The Japanese team remains silent throughout the presentation and doesn’t provide immediate feedback.
Questions
- Why might the Japanese team remain silent?
- How could this silence be interpreted differently by the American and Japanese teams?
- What strategies could the American team use to improve communication in this situation?
| Part C: Role-Playing Activity Instructions Choose a cross-cultural business meeting between representatives from two different countries. As a pair, choose from: – United States and Japan – Brazil and Germany – India and Australia Everyone can communicate in the same language. Scenario You’re discussing a potential business partnership. Research the basic cultural norms for your assigned country and incorporate them into the role-play. Topics you could Cover – Greetings and introductions – Eating and drinking – Presenting your business proposal – Negotiating terms – Handling disagreements – Concluding the meeting Reflection After the role-play, discuss: 1. What challenges did you face in communicating across cultures? 2. What strategies did you use to overcome these challenges? 3. What did you learn about effective cross-cultural communication? |
Conclusion
Effective cross-cultural communication requires awareness, knowledge, and practice. By completing this activity, you’ve taken important steps towards improving your cross-cultural communication skills. Remember, these skills are valuable not only in business settings but in all aspects of our increasingly interconnected world.
Final Quiz – Cross-Cultural Interactions
Cross-Cultural Interactions Quiz
This multiple-choice quiz will test your knowledge about cross-cultural interactions and their effects on our global society. Choose the best answer for each question.

Extension Activity: Cross-Cultural Cooking
Overview
This lesson plan explores the culinary exchanges that occurred during the colonial era, with a focus on how ingredients and cooking techniques from different cultures influenced each other. You will learn about the historical context of colonial trade and migration, and how these factors shaped the development of fusion cuisines.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Understand the impact of colonialism on global cuisine
- Identify key ingredients and dishes that resulted from colonial cross-cultural exchanges
- Analyze how the Silk Road-inspired bread recipe reflects historical trade routes and cultural fusion