The Global Tapestry of The Americas (1200 to 1450)
The Americas
Conventionally there are four main geographical regions or subregions in the Americas.
- North America
- The Caribbean
- Central America
- South America
Area
Area: 42.55 million km² (16,428,000 sq mi)
Coverage: 8.3 percent of Earth’s surface area and 28.5 percent of its total land area.
Largest Countries:
Canada: 9,984,670 km²
The United States: 9,833,517 km²
Brazil: 8,515,770 km²
Argentina: 2,780,400 km².
The Smallest Independent Country:
Saint Kitts and Nevis: 261 km².
How many countries are there in the Americas?
America is shared by 35 countries (sovereign states) and several dependent territories.
Introduction to Post-Classical Americas
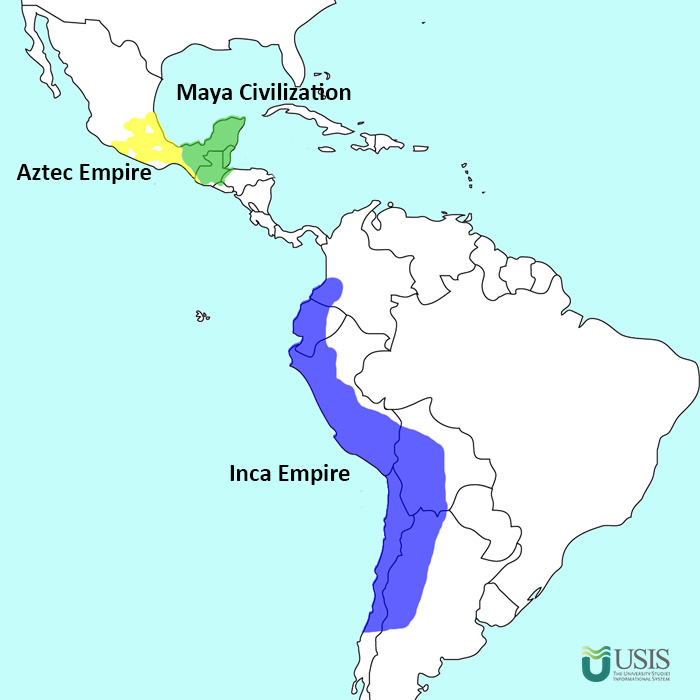
Maya, Inca, and Aztecs were three remarkable civilizations that thrived in the southern parts of America at different points in history.
The Maya civilization, known for its amazing calendar that accurately predicted events such as floods and eclipses, holds a prominent place among these civilizations.
The Aztecs and Incas also contributed immensely to America with their culture, heritage, power, and intelligence.
The Inca Empire
This is the background music for you to listen to while you learn about the Inca Empire.
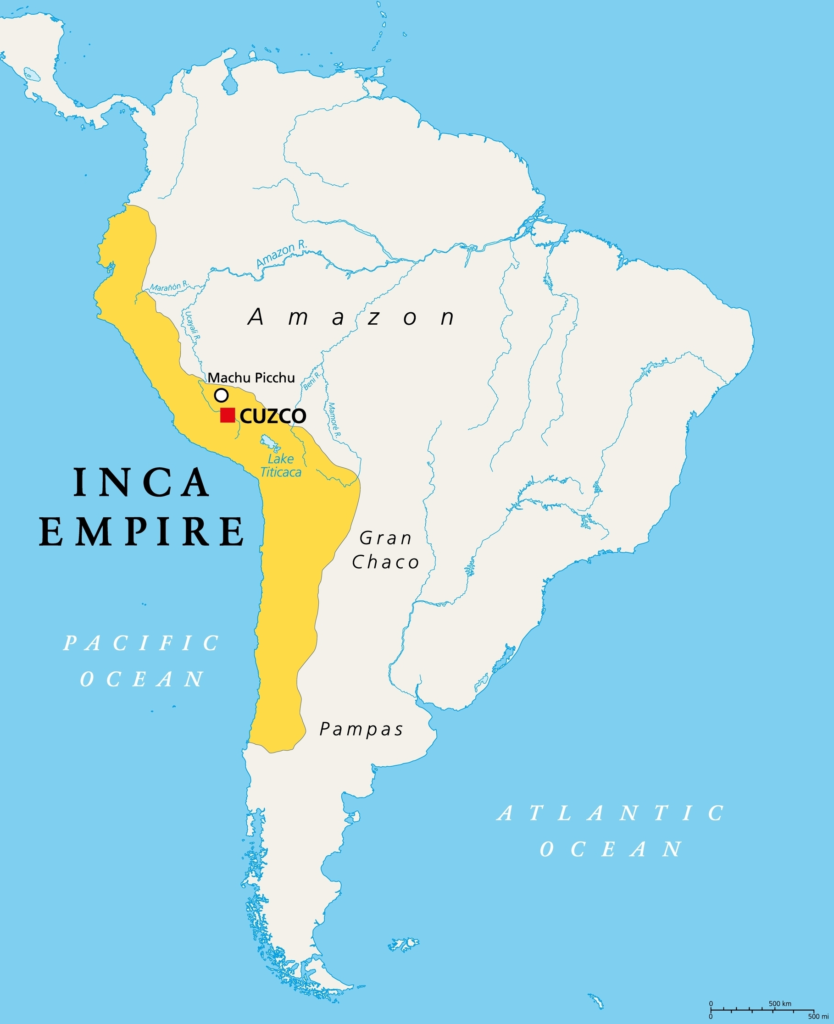
Around the year 1200, the Inca civilization (called Tawantinsuyu – the “Realm of the Four Parts”) settled in central Peru of South America and also parts of Ecuador, Bolivia, Columbia, Chile, and Argentina. The Inca Empire, was the largest empire in pre-Columbian* America. It extended approximately 2500 miles (4000 km) from north to south. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The population was around 16 million people and they were famous for their impressive stonework and temples made without mortar (a mixture of cement and sand).
*In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original peopling of the Americas in the Upper Paleolithic to European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus’s voyage of 1492.
Region
The Inca Empire broadly covered Peru and Chile, and parts of Bolivia and Argentina.
The number of people inhabiting Tawantinsuyu at its peak is uncertain, with estimates ranging from 4–37 million. Most population estimates are in the range of 6 to 14 million. In spite of the fact that the Inca kept excellent census records using their quipus, knowledge of how to read them was lost as almost all fell into disuse and disintegrated over time or were destroyed by the Spaniards.
Andes Mountains
The Andes Mountains is an extensive chain of mountains and peaks that covers a length of 8,500 km. It is the largest in the world. It crosses seven countries in South America: Peru, Bolivia, Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Chile and Argentina. The Incas adapted to the challenging geography of the Andes Mountains.
Inca Road System
The Inca road system (meaning “royal road” in Quechua) was the most extensive and advanced transportation system in pre-Columbian South America. It was about 40,000 km (25,000 mi) long. The construction of the roads required a large expenditure of time and effort.
Terrace Farming
Quechua
Quechua , also called Runasimi (“people’s language”) is an indigenous language family that originated in central Peru and thereafter spread to other countries of the Andes. It is today the most widely spoken pre-Columbian language family of the Americas, with the number of speakers estimated at between 7 and 10 million speakers. Approximately 13.9% (3.7 million) of Peruvians speak a Quechua language.
Although Quechua began expanding many centuries before the Incas, it was the primary language family within the Inca Empire. Quechua languages are still widely spoken today, being co-official in many regions and the most spoken language lineage in Peru, after Spanish.
MIT’A System
Mit’a was a form of tribute to the Inca government in the form of labor. This mandatory labor was used instead of monetary taxes; a tax labor. This tax labor accounted for much of the Inca state tax revenue; beyond that, it was used for the construction of the road network, bridges, agricultural terraces, and fortifications in ancient Peru. Military service was also mandatory.
All males starting at the age of fifteen were required to participate in the mit’a to do public services. This remained mandatory until the age of fifty. However, the Inca rule was flexible on the amount of time one could share on the mit’a turn. Overseers were responsible to make sure that a person after fulfilling his duty in the mit’a still had enough time to care for his own land and family.
Quipa
Quipu (also spelled khipu) are recording devices fashioned from strings historically used by a number of cultures in the region of Andean South America.
A quipu usually consisted of cotton or camelid fiber strings.
The Inca people used quipu for collecting data and keeping records, for monitoring tax obligations, for collecting census records, for calendrical information, and for military organization. The cords stored numeric and other values encoded as knots.
A quipu could have only a few or thousands of cords. A relatively small number have survived.
Activities
Learn about Quipas
Make a Quipa. Think of an important number or dates, or count things that could be added to a quipa. Use the base ten system of the quipa and include some meaningful color coding.
(From: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/Patrick-Dempsey)
(From: https://victoriarestrepo.com/)
The Aztec Empire
This is the background music playlist for you to listen to while you learn about the Aztec Empire.

The Aztecs were a Mesoamerican* culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. It grew in the Valley of Mexico from 1300 to 1521 with a good environment for agriculture due to its moderate climate and rich natural resources. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. The Aztec capital, named Tenochtitlan, was the largest city. The Aztecs were famous for their farming, warfare, and temple-building skills. They were also famous for their diverse culture, beautiful sculptures, and advances in many other aspects.
*Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and small parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and Costa Rica.
The Aztec Chinampas Garden System
The Maya Civilization
This is the background music for you to listen to while you learn about the Maya Civilization.

The Maya civilization was a Mesoamerican civilization that existed from antiquity* to the early modern period. It appeared around 2600 B.C. in southeastern tropical parts of Honduras and El Salvador. It is known by its ancient temples and glyphs (script). The Maya people had a highly advanced culture; the Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. The civilization is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. They lived in farming villages on the Yucatan Peninsula and the southern highlands.
*Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BC – AD 750.
Activities
Tour The Ancient World of The Americas.
https://earth.google.com/earth/d/1JXODAexHDQsbXRqPhVsDxhiaiMya3TFX?usp=sharing
You are going to have a quiz based entirely on this map so spend some time exploring.
Which Ancient American are You?